The rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has driven dramatic changes in hardware design. Traditional processors — CPUs and GPUs — are flexible and powerful but not always optimal for AI tasks. This gap has led to the development of a specialized class of chip called a Neural Processing Unit (NPU), dedicated to accelerating AI workloads with higher efficiency and lower power consumption.

What Is an NPU?
A Neural Processing Unit (NPU) is a hardware accelerator designed to perform neural network computations efficiently. These computations include tasks like matrix multiplications, convolution operations, and other common functions used in deep learning algorithms. NPUs are optimized to process these operations many times faster and more energy‑efficiently than general‑purpose CPUs or even GPUs.
Unlike CPUs that handle a wide range of tasks or GPUs that excel at parallel processing for graphics and general compute, NPUs are narrowly focused on machine learning workloads — delivering significant performance gains where it matters most.
How NPUs Work
At their core, NPUs are built to execute large numbers of mathematical operations in parallel, especially those found in AI models like:
- Matrix multiplication — the foundation of neural networks
- Convolutions and feature extraction — common in vision models
- Activation functions and other nonlinear computations
The internal architecture often includes many tiny compute units grouped into tiles, along with local memory and controllers that schedule data flow without bogging down the main CPU.
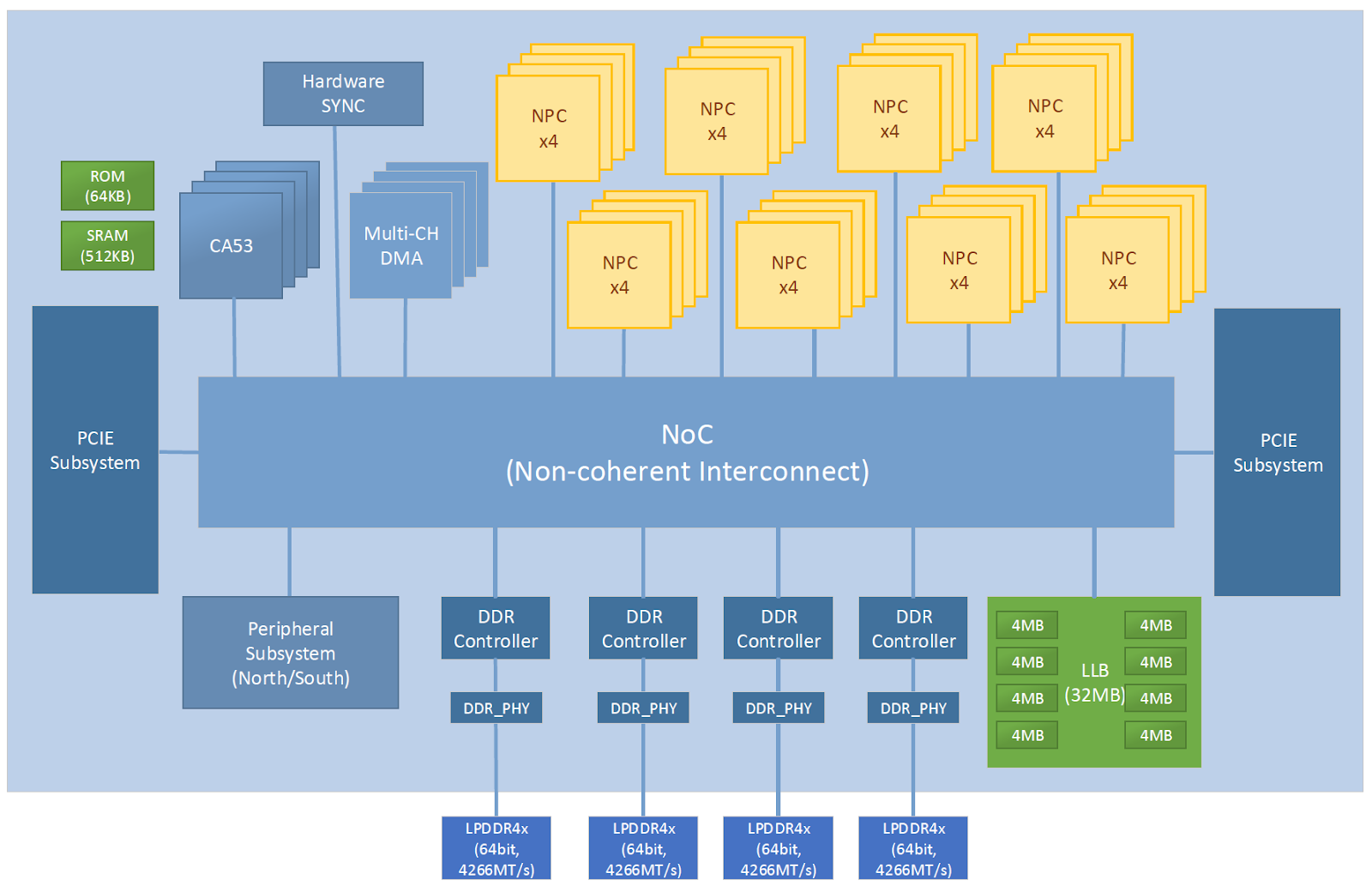
NPUs vs CPUs and GPUs
Each processor type has a role:
- CPU — great generalist processor
- GPU — excels at parallel tasks, especially graphics and general compute
- NPU — specialized for neural networks and AI inference
NPUs achieve faster inference speeds and lower energy usage compared to CPUs and often even GPUs when performing AI‑specific tasks. CPUs must handle control logic and branching instructions, while GPUs — though highly parallel — are still general compute engines. NPUs focus on what matters most to AI: quick execution of neural network models.
Real‑World Applications of NPUs
NPUs are becoming increasingly common across industries:
- Smartphones — real‑time face recognition, image processing, and voice assistants
- Edge devices — IoT sensors and smart cameras performing AI locally
- Autonomous systems — on‑device decision‑making in robots and vehicles
- Laptops — dedicated AI acceleration for local machine learning tasks

NPUs are especially important for applications that must run AI without relying on cloud servers — improving responsiveness and privacy while reducing data transmission costs.
The Future: Efficient and Embedded AI
As AI models become larger and more complex, NPUs will continue to play a key role in ensuring that they run efficiently. Advances in microarchitecture aim to:
- Scale AI performance without large power budgets
- Support more complex models in real time
- Integrate smoothly with CPUs and GPUs on the same chip
Whether in mobile devices, embedded systems, or next‑gen computers, NPUs represent the hardware frontier of efficient AI acceleration — making advanced intelligence faster, more accessible, and less dependent on the cloud.
Comments
There are currently no comments on this article.
Comment